Weather Modification: Cloud Seeding in Oman
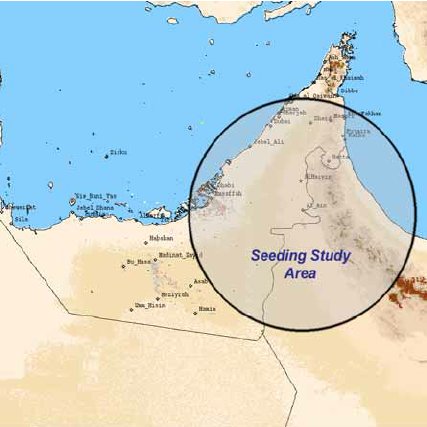
With the decline in water resources in the country, experts have been trying various methods to find sustainable water resources and increase rainfall to meet the growing demands of the population.A weather modification method known as cloud seeding was introduced after various trials over the eastern and western Hajar mountains.
The Al Hajar Mountains, an important source of groundwater for both the UAE and Oman, creates two very different climatic zones on either side, separating the coastal plains from the western desert area.With peaks reaching up to 3075 meters along the eastern coast of the peninsula, the vegetation includes scrublands and woodlands at the bottom and fruit cultivation being carried out in the valleys. Energy fluxes occur due to the contrasting landscape along with the presence of altocumulus middle-altitude (clouds in the middle levels of air), atmospheric conditions, sea breezes and convective developments, thereby triggering thunderstorms. 
Among the four weather systems present, summer was chosen as the best season for testing weather modification methods as convective clouds during this time hold the best capacities for cloud seeding. The wind convergence in the area also contributes to a suitable environment for this modification method.
Two cloud seeding methods have usually been used across various countries, namely glaciogenic, cold-cloud seeding using dry ice and silver iodide and hygroscopic, warm-cloud seeding with hygroscopic flares which has showed better results over the Al Hajar Mountains as compared to the former method.Care has to be taken to wisely use such chemicals as in large quantities they have proved to be toxic.In addition, these chemicals also deprive areas downwind of rains if over used, leading to geo-political spats.
With the UAE benefitting from the cloud seeding method in the late 90s, the Sultanate began studying the regional weather pattern and started to work on the project from the year 2012 in several areas including Al Jabal AL Akhdar and the Dhofar Governorate. Ion emission technology, considered one of the safest technologies, using ionic emitters in 12 cloud seeding stations was installed.These emitters sent negative ions to coalesce with dust particles using rising air currents and increase rainfall.
Over a period of five years, the project was monitored and the results were evaluated by the University of Wollongong in Australia.The results showed an impressive 18.8% increase in rainfall rates with an accuracy of 99.99 per cent.
The Supreme Council of Planning (SCP) which monitors the country’s commitment towards the Sustainable Development Goals on behalf of the Government of Oman has taken this initiative to ensure Oman’s growing needs for freshwater resources in a sustainable manner.
For a downloadable copy:Cloud Seeding in Oman